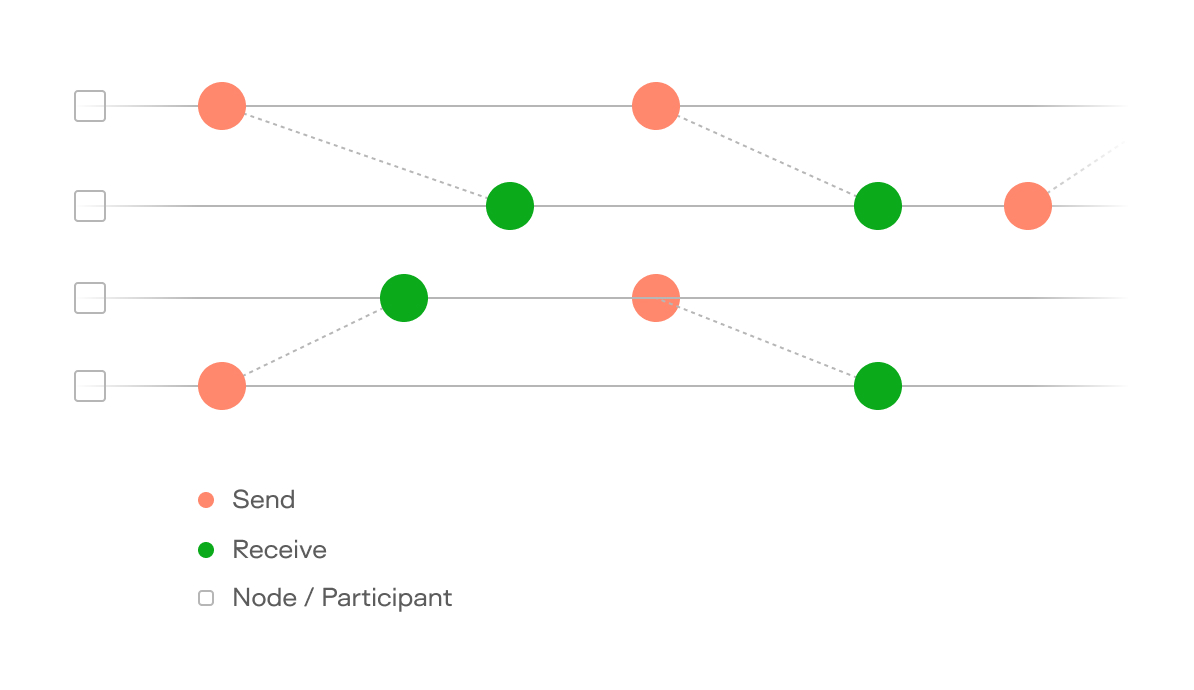
Data Structure
Keeta's approach to blockchain technology centers around its use of a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) structure, representing a departure from traditional blockchain architectures.
In this system, transactions are linked in a multi-dimensional web rather than a single, linear chain, allowing for parallel processing that increases the network's throughput and scalability.
Unlike traditional blockchains, which struggle with scalability issues due to their linear nature and sequential transaction processing, Keeta's DAG system can handle a high volume of transactions simultaneously. This parallel processing eliminates the bottlenecks that plague traditional systems as network activity increases, enabling Keeta Network to scale efficiently as it grows.